Created
: 2025.06.21













![]() 2025.06.21 00:17
2025.06.21 00:17
The US Dollar Index (DXY) is trading sideways on Friday, holding above 98.00, as markets digest this week's key geopolitical and monetary policy developments.
While rising tensions in the Middle East have kept risk appetite in check, gains for the Greenback remain limited amid growing expectations for Federal Reserve (Fed) rate cuts this year.
Investors remain on edge following reports that President Trump has given himself a two-week window to decide whether the US will join Israel in launching military action against Iran.
The move allows time for ongoing European-led negotiations in Geneva to play out, but this also raises the stakes if diplomacy fails. The uncertainty has helped the US Dollar find modest support as a safe-haven asset.
Despite the short-term lift, the broader outlook for the US Dollar remains clouded. The Fed left interest rates unchanged this week, but Chair Jerome Powell struck a cautious tone, emphasizing the importance of data dependency and the potential risks of inflation associated with tariffs. Markets are still pricing in a potential rate cut as early as September.
Adding to the complexity is the growing divergence in global monetary policy. The Swiss National Bank and Norges Bank surprised markets with rate cuts, while the European Central Bank, Bank of England, and Reserve Bank of Australia remain on hold but are increasingly dovish. This policy gap has created temporary support for the US Dollar through yield differentials, although sentiment remains fragile.
Technically, the DXY is struggling to build momentum. The index is clinging to its 20-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at 98.91, with the 50-day SMA at 99.50 adding to upside resistance. Key support lies near 97.61, the low of the January to June range.
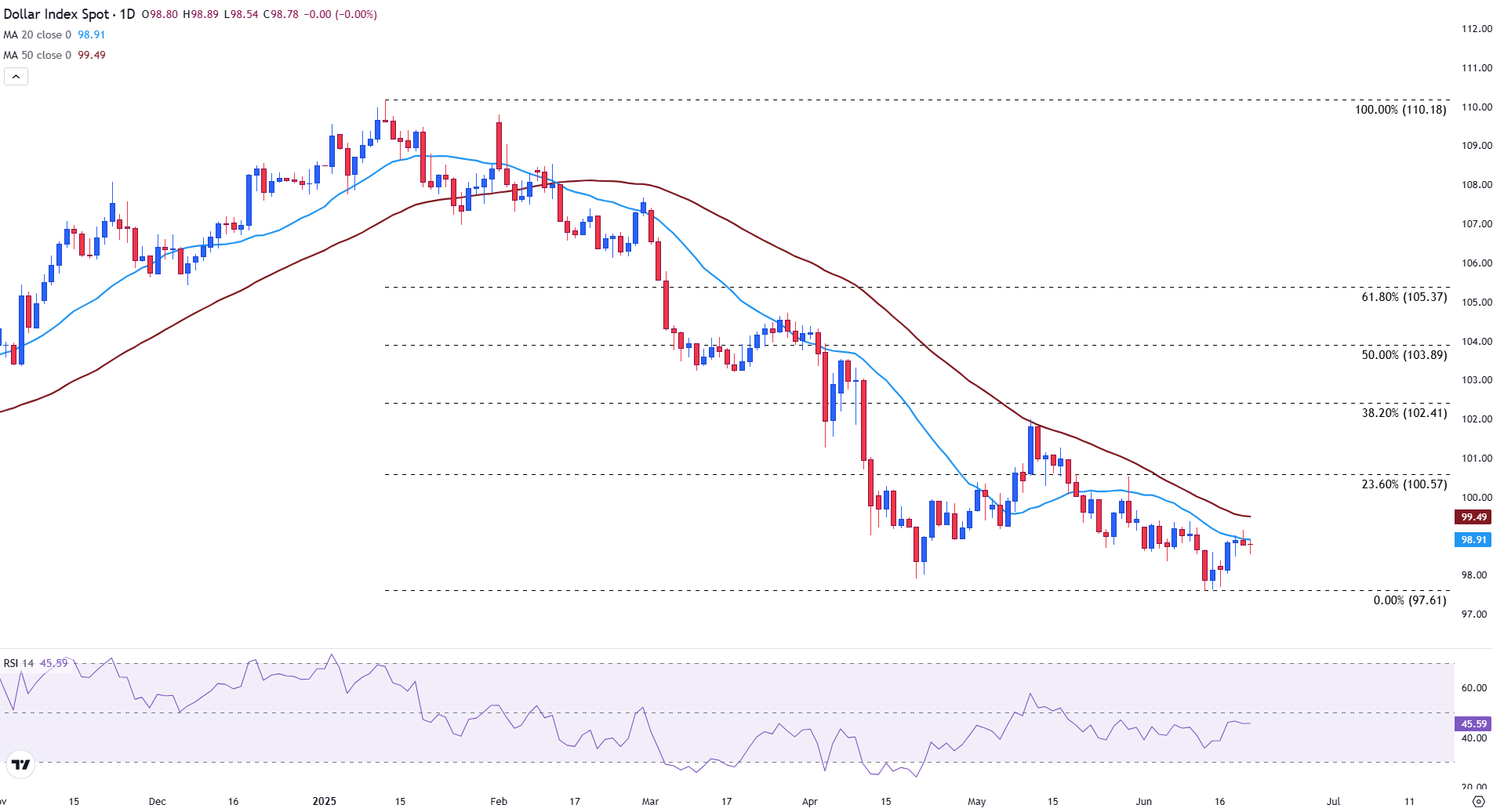
On the upside, the 100.00 psychological level and the 23.6% Fibonacci retracement at 100.57 remain critical hurdles. Momentum also appears muted, with the Relative Strength Index (RSI) at 46, still below the neutral 50 mark.
Unless the Dollar Index can break decisively above the 99.50-100.57 zone, the broader downtrend is likely to persist as traders balance safe-haven flows against the prospect of Fed easing and shifting global risk sentiment.
The US Dollar (USD) is the official currency of the United States of America, and the 'de facto' currency of a significant number of other countries where it is found in circulation alongside local notes. It is the most heavily traded currency in the world, accounting for over 88% of all global foreign exchange turnover, or an average of $6.6 trillion in transactions per day, according to data from 2022. Following the second world war, the USD took over from the British Pound as the world's reserve currency. For most of its history, the US Dollar was backed by Gold, until the Bretton Woods Agreement in 1971 when the Gold Standard went away.
The most important single factor impacting on the value of the US Dollar is monetary policy, which is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability (control inflation) and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these two goals is by adjusting interest rates. When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed's 2% target, the Fed will raise rates, which helps the USD value. When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates, which weighs on the Greenback.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve can also print more Dollars and enact quantitative easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used when credit has dried up because banks will not lend to each other (out of the fear of counterparty default). It is a last resort when simply lowering interest rates is unlikely to achieve the necessary result. It was the Fed's weapon of choice to combat the credit crunch that occurred during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy US government bonds predominantly from financial institutions. QE usually leads to a weaker US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing in new purchases. It is usually positive for the US Dollar.
![]()
Created
: 2025.06.21
![]()
Last updated
: 2025.06.21

FXStreet is a forex information website, delivering market analysis and news articles 24/7.
It features a number of articles contributed by well-known analysts, in addition to the ones by its editorial team.
Founded in 2000 by Francesc Riverola, a Spanish economist, it has grown to become a world-renowned information website.
We hope you find this article useful. Any comments or suggestions will be greatly appreciated.
We are also looking for writers with extensive experience in forex and crypto to join us.
please contact us at [email protected].
Disclaimer:
All information and content provided on this website is provided for informational purposes only and is not intended to solicit any investment. Although all efforts are made in order to ensure that the information is correct, no guarantee is provided for the accuracy of any content on this website. Any decision made shall be the responsibility of the investor and Myforex does not take any responsibility whatsoever regarding the use of any information provided herein.
The content provided on this website belongs to Myforex and, where stated, the relevant licensors. All rights are reserved by Myforex and the relevant licensors, and no content of this website, whether in full or in part, shall be copied or displayed elsewhere without the explicit written permission of the relevant copyright holder. If you wish to use any part of the content provided on this website, please ensure that you contact Myforex.
Myforex uses cookies to improve the convenience and functionality of this website. This website may include cookies not only by us but also by third parties (advertisers, log analysts, etc.) for the purpose of tracking the activities of users. Cookie policy