Created
: 2024.09.19













![]() 2024.09.19 05:38
2024.09.19 05:38
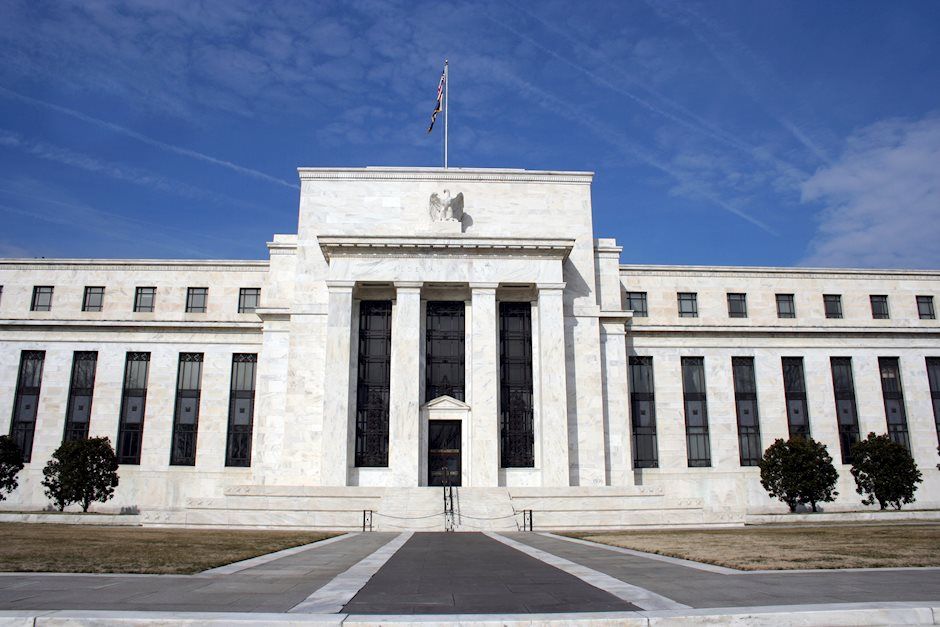
The US Federal Reserve (Fed), easily the largest and most powerful central bank in the world, just decreased its Federal Funds Interest Rate by 50 basis points (bps) to a reference range of 5.0-5.25% percent. This is the first time that the US interest rate has been cut since March of 2020 and represents a major policy shift for the Fed.
The US Fed, headed by Fed Chairman Jerome Powell, cut interest rates for the first time in four years in order to alleviate pressure underpinning the US economy and help keep the largest economic region in the world healthy. Interest rates impact a wide range of economic aspects, including how much it costs to borrow money to finance business operations. With interest rates easing, businesses may be more inclined to step up their pace of borrowing and explore more hiring and production activities. Also, consumers may be more inclined to increase their level of spending on a credit basis, both because it will be slightly easier to obtain bank-funded credit, and also because saving their money will have a slightly less-attractive rate of return versus going ahead and spending it. In this way, central banks can discourage consumers from actively saving more money than they otherwise would have by making the rate of return on savings less attractive, pushing more money into the domestic economy.
As the US central bank, the Federal Reserve has a dual mandate: control the rate of domestic inflation using a variety of policy tools, and also maintain stable employment numbers within the US. Since falling interest rates tend to have an immediately inflationary effect, the Fed needs to be careful about how fast and how much they raise or lower interset rates. September's rate cut implies that the Fed believes it has successfully tamed US consumer inflation, and expects headline price growth figures to continue easing back toward the Fed's internal goal of 2% YoY inflation. US employment figures also play a role in Fed decision-making on interest rates, as too high of a reference rate for too long could discourage business activity to the point that a wide sweep of layoffs could force a hiccup into the economy, increasing the likelihood of a recession.
With the Fed's first rate cut in four years finally out of the way, investors will be immediately pivoting to guess whether the Fed will cut rates again when the central bank gathers on November 7 to deliver another rate call. It is still too early to tell what the Fed's next move is going to be, and policymakers will want to wait and see what the next few batches of economic data say before making any decisions a little under two months from now.
Monetary policy in the US is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these goals is by adjusting interest rates. When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed's 2% target, it raises interest rates, increasing borrowing costs throughout the economy. This results in a stronger US Dollar (USD) as it makes the US a more attractive place for international investors to park their money. When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates to encourage borrowing, which weighs on the Greenback.
The Federal Reserve (Fed) holds eight policy meetings a year, where the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) assesses economic conditions and makes monetary policy decisions. The FOMC is attended by twelve Fed officials - the seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the remaining eleven regional Reserve Bank presidents, who serve one-year terms on a rotating basis.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve may resort to a policy named Quantitative Easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the Fed's weapon of choice during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy high grade bonds from financial institutions. QE usually weakens the US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process of QE, whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing, to purchase new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US Dollar.
![]()
Created
: 2024.09.19
![]()
Last updated
: 2024.09.19

FXStreet is a forex information website, delivering market analysis and news articles 24/7.
It features a number of articles contributed by well-known analysts, in addition to the ones by its editorial team.
Founded in 2000 by Francesc Riverola, a Spanish economist, it has grown to become a world-renowned information website.
We hope you find this article useful. Any comments or suggestions will be greatly appreciated.
We are also looking for writers with extensive experience in forex and crypto to join us.
please contact us at [email protected].
Disclaimer:
All information and content provided on this website is provided for informational purposes only and is not intended to solicit any investment. Although all efforts are made in order to ensure that the information is correct, no guarantee is provided for the accuracy of any content on this website. Any decision made shall be the responsibility of the investor and Myforex does not take any responsibility whatsoever regarding the use of any information provided herein.
The content provided on this website belongs to Myforex and, where stated, the relevant licensors. All rights are reserved by Myforex and the relevant licensors, and no content of this website, whether in full or in part, shall be copied or displayed elsewhere without the explicit written permission of the relevant copyright holder. If you wish to use any part of the content provided on this website, please ensure that you contact Myforex.
Myforex uses cookies to improve the convenience and functionality of this website. This website may include cookies not only by us but also by third parties (advertisers, log analysts, etc.) for the purpose of tracking the activities of users. Cookie policy